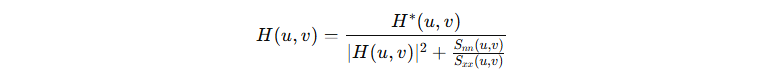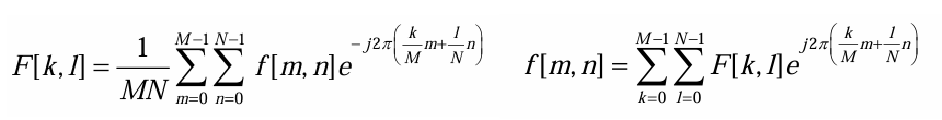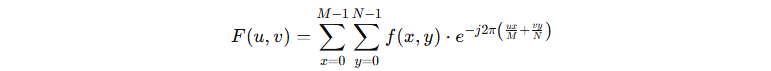유전 알고리즘(GA)은 최적화 문제에 활용될 수 있습니다. 당연히 영상처리 기술들에도 적용이 가능하며, 윤곽선 검출에 대표 기술 중에 하나인 캐니 엣지 탐색(Canny Edge Detection)에 적용해 보겠습니다. 캐니 엣지 탐색 방법에서는 윤곽선 검출을 위해 두 개의 임계값인 Threshold1과 Threshold2를 사용하며, Threshold1 이하는 엣지가 아닌 영역이며 Threshold2 이상은 엣지영역으로 구분하고 Thresholds의 사이는 Canny Procedure에 의해 엣지 유무를 판단하게 됩니다.
2025.10.26 - [영상처리 기술] - 영상처리 유전 알고리즘 Genetic Algorithm 이해
2018.01.15 - [영상처리 도구] - OpenCV 윤곽선 검출 Edge Detection
유전 알고리즘의 기본과 윤곽선 검출에 대해서는 기존 블로그를 참고해 보시면 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 아래는 OpenCV와 파이썬을 활용한 캐니 엣지 탐색 알고리즘의 파라미터 Threshold1과 Threshold2 최적화 예제입니다. 개체(염색체)는 [Threshold1, Threshold2]로 설정이 되고 적합도(Fitness) 평가에는 당연히 캐니 엣지 탐색 방법과 그 윤곽선 수로 Score를 계산합니다.
기존 블로그에서도 언급을 했지만 반복 수행을 통해 최적해를 찾는 점과 교차율과 돌연변이율 등 매개변수 설정이 있다는 것은 설정 차이를 통해 Solution에 차이가 생길 수 있다는 점을 인식해야 하며 이런 이유로 항상 최적해를 보장하지 않는다는 점을 알고 유전 알고리즘을 활용해야 합니다.
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
# ------- gray image read ---------
img = cv2.imread('image.tif', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# ------ 1. fitness define ------------
def fitness(threshold1, threshold2):
edges = cv2.Canny(img, threshold1, threshold2)
score = np.sum(edges > 0) # total number of edges
return score
# --------2. initialization --------------
def random_chromosome():
return [random.randint(0, 100), random.randint(100, 255)] # [t1, t2]
population_size = 20
population = [random_chromosome() for _ in range(population_size)]
# ------ 3. GA parameters --------------
generations = 30
mutation_rate = 0.2
# ------- 4. repetition ----------------
for gen in range(generations):
fitness_scores = [fitness(ch[0], ch[1]) for ch in population] # fitness calc.
# selection (선택)
sorted_pop = [x for _, x in sorted(zip(fitness_scores, population), reverse=True)]
parents = sorted_pop[:int(population_size/2)]
# Crossover (교차)
children = []
while len(children) < population_size - len(parents):
p1, p2 = random.sample(parents, 2)
cross_point = random.randint(0, 1)
child = p1[:cross_point+1] + p2[cross_point+1:]
children.append(child)
# Mutation (돌연변이)
for child in children:
if random.random() < mutation_rate:
idx = random.randint(0, 1)
child[idx] = random.randint(0, 255)
# Replacement (대체)
population = parents + children
# best sol
best_fit = max(fitness_scores)
best_chrom = population[np.argmax(fitness_scores)]
print(f"세대 {gen+1}: 최고점 ={best_fit}, 임계값={best_chrom}")
# ------- display --------------------
best_t1, best_t2 = best_chrom
best_edge = cv2.Canny(img, best_t1, best_t2)
cv2.imshow("Canny Best Edges", best_edge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
'영상처리 기술' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 영상처리 유전 알고리즘 Genetic Algorithm 이해 (0) | 2025.10.26 |
|---|---|
| 영상처리 웨이블릿 변환 Wavelet Transform 활용: 잡음 제거 (0) | 2025.10.12 |
| 영상처리 웨이블릿 변환 Wavelet Transform: 시간-주파수 분석 (0) | 2025.10.05 |
| 영상처리 위너 필터(Wiener Filter) 이해와 기본 (0) | 2025.09.28 |
| 대규모 언어모델 (LLM: Lage Language Model)의 이해와 활용 (0) | 2025.09.21 |